【基礎知識】乃木坂46の「いつかできるから今日できる」を数学的命題として解釈する
- 命題
基礎知識
公式
三角比に関する公式はとても多く、しかも覚えにくいという特徴があります。
しかし、それは単純暗記に頼ってしまうことが原因です。
三角比に限ったことではありませんが、各種公式の導出方法自体を覚え、その場で公式の導出を行えるような実力をつけることを目指しましょう。
どの公式もそうなのですが、$\tan \theta$に対する公式は、$\tan \theta = \cfrac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta}$を利用して導出することが一般的です。
そのため、まずは$\sin \theta$と、$\cos \theta$に対する公式を求めることとなります。
次のような図を考えます。
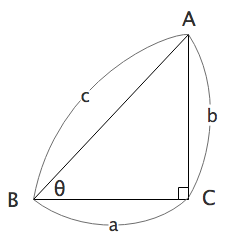
三角形の内角の和は$180^\circ$なので、
$$\begin{array}{rcl} \angle A + \angle B + \angle C &=& 180^\circ \\\\ \angle A + \theta + 90^\circ &=& 180^\circ \\\\ \angle A &=& 90^\circ -\theta \end{array}$$となります。
三角比の定義から、
$$\begin{align} \sin \theta &=& \cfrac{b}{c} \end{align}$$ $$\begin{align} \cos \theta &=& \cfrac{a}{c} \end{align}$$ $$\begin{align} \tan \theta &=& \cfrac{b}{a} \end{align}$$同様に、
$$\begin{align} \sin (90^\circ -\theta) &=& \cfrac{a}{c} \end{align}$$ $$\begin{align} \cos (90^\circ -\theta) &=& \cfrac{b}{c} \end{align}$$ $$\begin{align} \tan (90^\circ -\theta) &=& \cfrac{a}{b} \end{align}$$(2)(4)より、
$$\begin{array}{rcl} \sin (90^\circ – \theta) &=& \cos \theta \end{array}$$(1)(5)より、
$$\begin{array}{rcl} \cos (90^\circ – \theta) &=& \sin \theta \end{array}$$(3)(6)より、
$$\begin{array}{rcl} \tan (90^\circ – \theta) &=& \cfrac{1}{\tan \theta} \end{array}$$以上により、
が証明されました。
次の図のような単位円を考えましょう。
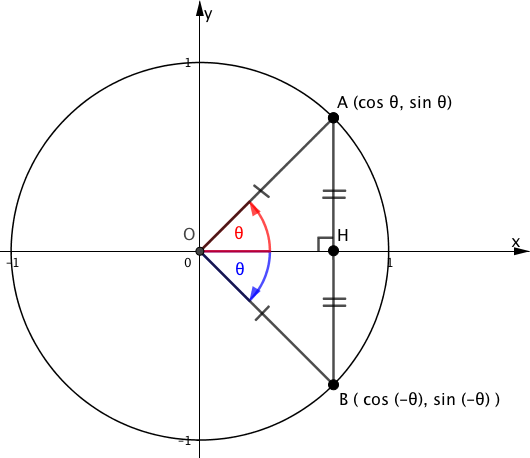
動径$\theta$の正の向きは反時計回りと一般的に決められているので、青色の$\theta$は$- \theta$を意味しています。
よって、点Bの座標は$( \cos ( – \theta) ,\sin ( – \theta) )$となります。
また、辺OHは$\angle AOB$の二等分線であり、△$OAB$は二等辺三角形なので、「二等辺三角形の頂角の二等分線は底辺を垂直に二等分する」ことにより、
となります。
よって、△$OAH$と△$OBH$はx軸に関して対象な図形となり、
$$\begin{array}{rcl} \sin (- \theta) &=& -\sin \theta \\\\ \cos (- \theta) &=& \cos \theta \end{array}$$が成り立ちます。
上の結果と、$\tan \theta = \cfrac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta}$より、
よって、
であることが証明されました。
次の図のような単位円を考えましょう。
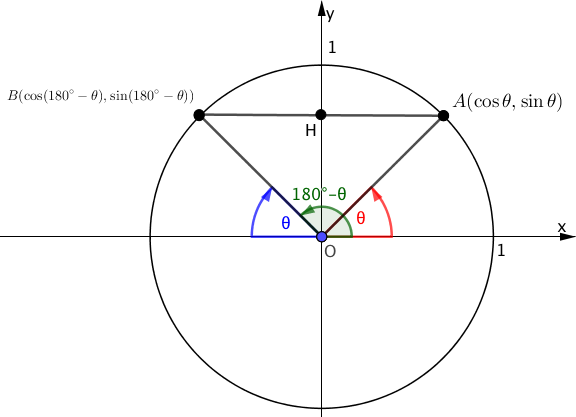
$- \theta $の三角比で証明した内容と同様にして、△$OAH$と△$OBH$はy軸に関して対象な図形となります。
これにより、
$$\begin{array}{rcl} \sin (180^\circ- \theta) &=& \sin \theta \\\\ \cos (180^\circ- \theta) &=& – \cos \theta \end{array}$$が成り立ち、
$$\begin{array}{rcl} \tan (180^\circ – \theta) &=& \cfrac{\sin (180^\circ – \theta)}{ \cos (180^\circ – \theta)} \\\\ &=& \cfrac{\sin \theta}{- \cos \theta} \\\\ &=& – \tan \theta \end{array}$$よって、
であることが証明されました。
その他の公式については後日公開の予定です。
【三角比】三角比のまとめ
この記事が気に入ったら
「いいね」しよう!
-このサイトの記事を書いている人-

某国立大工学部卒のwebエンジニアです。
学生時代に塾講師として勤務していた際、生徒さんから「解説を聞けば理解できるけど、なぜその解き方を思いつくのかがわからない」という声を多くいただきました。
授業という限られた時間の中ではこの声に応えることは難しく、ある程度の理解度までに留めつつ、繰り返しの復習で覚えてもらうという方法を採らざるを得ないこともありました。
本ブログでは「数学の問題を解くための思考回路」に重点を置いています。
それらを通じて自らの力で問題を解決する力が身につくお手伝いができれば幸いです。
>> お問い合わせ
>> プライバシーポリシー